
CMRL TU-02 –
Rising above underground challenges
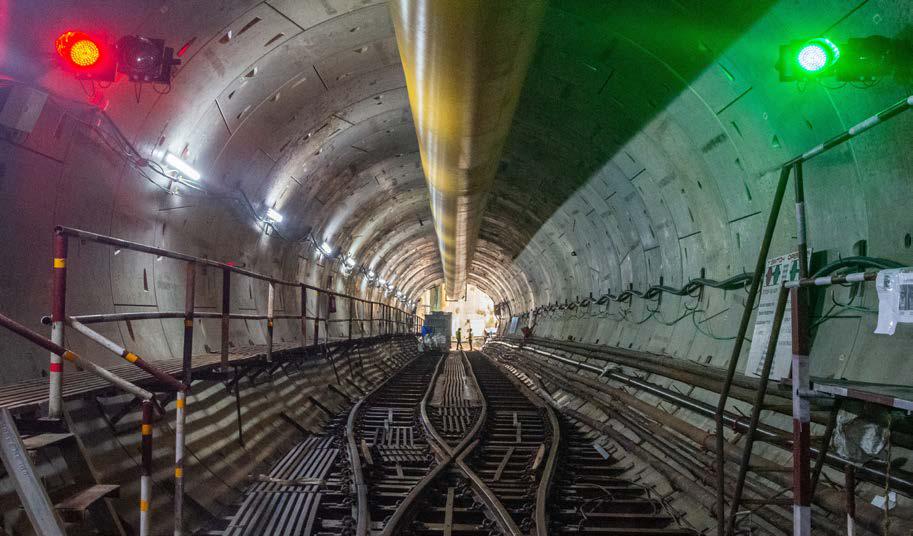
The Chennai Metro Rail Limited TU-02 project has several claims to fame: it involves the construction of twin tunnels of 12.5 kms each, Diaphragm walls for 4 underground stations, precasting of 18,000 tunnel rings and for the first time in India, simultaneous deployment of 8 TBMs (32 drives) and the creation of an in-house facility to re-manufacture TBMs.

Awarded in June 2021, Task Force Leader, H Jayarama, agrees that driving progress has been so much easier with the help of technology. “In TU-02, we have achieved 100% implementation of several digital initiatives,” he says. “In addition, as a part of innovation and digitalization, we are implementing automatic concrete distribution system, automatic segment cage making system, lean management practices, BIM implementation up to 4D, Geofreq – GIS integrated platform for instrumentation monitoring of tunnelling, to improve safety, quality, and productivity.”

Automatic Concrete Distribution System
A 300 m x 25 m casting shed featuring 108 segment moulds (18 sets) is the location for rebar cage making concreting and steam curing of tunnel rings. The cycle time for concreting one mould was initially 35 minutes. An additional safety issue was the movement of transit mixers on a 5 m wide road within the shed. “These have been addressed by our Automated Concrete Distribution System,” highlights Project Manager, Ahmet Ozturk. “Now, the concrete is supplied to moulds by shuttles moving on overhead tracks that has reduced our concreting cycle time to 20 minutes and wastage to 0%. It is sustainable too, for it has reduced 83 MT of carbon emissions and requirement of water by 6,900 KL.” He smilingly adds that the initiative has won plaudits from the Director of Projects, CMRL.

GeoFreq
“Tunnelling in a metro city below rivers, bridges, schools, residential and commercial buildings is challenging,” remarks Jayarama, “and to ensure safe progress, we must track settlement on the surface for the entire 12 kms by installing 10,000+ different Instruments like Building Settlement Markers and Optical Prisms.” Since real time monitoring of a humungous number of settlement readings was next to impossible, the project, IC Digital and engineering teams developed GeoFreq, a web-based database management application, placed on a GIS integrated platform for real-time geospatial monitoring of instruments. “With GeoFreq, engineers can easily carry out data analysis like Trend Analysis over time,” explains Task Force Lead, Planning & Monitoring, U Ashwetha. “It sends out automatic SMS and emails alerts to the engineers in case of any alarming settlement to take necessary course corrections.”
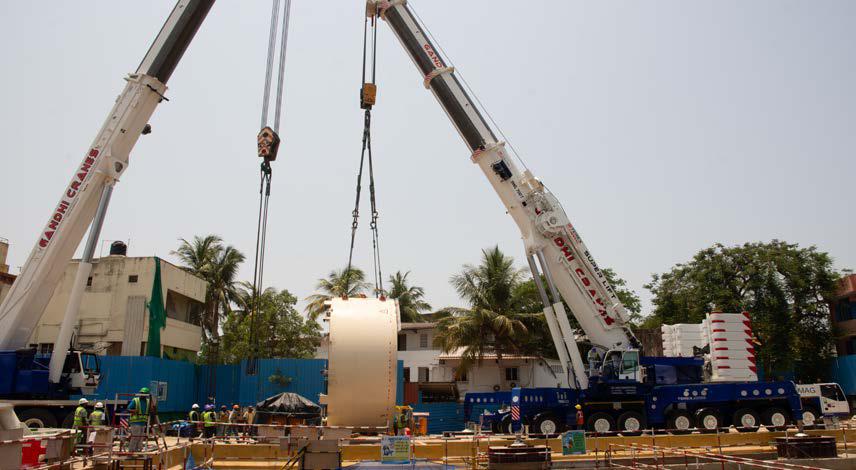


Tandem lifting and lowering of TBM
Tunnel Segment Management App
To manage the data of 1 lakh tunnel segments across the lifecycle from manufacturing to erection in the tunnel, the project team in collaboration with the IC Digital team, developed the user-friendly Tunnel Segment Management App that uses Passive IP 67 cast in RFID tags and barcodes to write and read using RFID technology in each segment across different steps from casting to erection. Casting Yard In-charge, Balamurugan, shares that the data will be available in the system for 15 years.
The user-friendly Tunnel Segment Management App uses Passive IP 67 cast in RFID tags and barcodes to write and read using RFID technology in each segment across different steps from casting to erection.
Other technology-led interventions
The Tunnel Access Management System uses biometrics to monitor tunnel entries & exits, workers are inducted using the WISA App, and concrete production monitored by the ConPro App.
Ashwetha adds to their list of technology interventions: Asset Insight to review machinery utilization & monitor diesel consumption, ProCube for progress monitoring, the Lab Inspection Management System to monitor lab reports & 4D BIM to monitor critical activities and plan & allocate resources.
A digital application to manage the inventory and consumption of the huge quantity of consumable materials of TBMs that are critical for operation, many of which are imported from different countries is in initial stage of implementation. “With 8 TBMs mining in different geologies and locations, it is imperative to ensure minimum inventory of critical material and track the consumption of each TBM drive wise,” points out Ahmet.
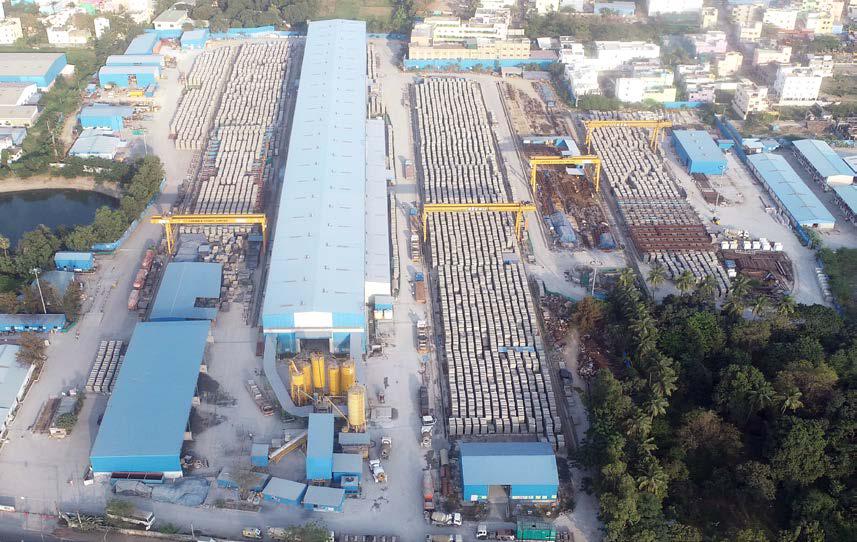

Bird’s-eye view of Precast Yard

“Our weekly review meetings are conducted in 4D integrated BIM models that help us to schedule our work and resources better, identify critical activities and arrive at solutions by collaborating with different teams including our Client and General Consultant team,” beams Deputy Project Manager, K P Senthilkumar. “I have found BIM to be a better collaboration and decision-making tool,” he adds for good measure. “The use of digital platforms has optimized the planning process and enhanced the team’s monitoring ability,” remarks Nalin M, Planning Manager. “The adoption of BIM has streamlined the construction process and encouraged greater collaboration among all stakeholders.”

With technology at the fore, it is no surprise that the CMRL TU 02 Project has been recognized as L&T’s Best Project in Digital Adoption & Benefits Realization in 2023.
With technology at the fore, it is no surprise that the CMRL TU 02 Project has been recognized as L&T’s Best Project in Digital Adoption & Benefits Realization in 2023 and Ashwetha sums up their efforts well. “The success of our digital journey is a result of a focused approach with continuous people engagement from inception, right through the developmental and implementation stages.”
RVNL Package 2
Enjoying encouraging ROI from apt digital solutions
L&T’s RVNL Package 2 project involves the construction of tunnels, bridges and formation works from Chainage 18+444 to 33+097 for a new Single Broad-Gauge Rail Link between Rishikesh and Karanprayag (totally 125 km) in Uttarakhand, India. The project undertaken by the Railway Ministry and running almost entirely through the Garhwal Himalayan range, will open easy access to the State’s pilgrimage centres, give a fillip to trade & commerce and uplift the economically underdeveloped areas along the line.
Project Manager, Rajesh Chopra’s drive has completed 76% of the 48-month project (plus 28 months of EOT granted) as of end June 2024 with delivery slated for December 2025.


“We have completed 25.3 km of excavation that is about 95% and 10 km of the lining that constitutes about 36% he apprises. Being executed using the NATM (New Austrian Tunnelling Method) technology, the key consideration of excavation in this method is that the underground structures are the load bearing structures wherein the ring like body is supported by the ground or rock mass. “While the major activity involved in NATM is blasting, the method is extremely flexible and adaptable to the changing ground conditions and cross sections with more room for optimization,” explains Rajesh. Additionally, the cost of drilling & blasting is lower as compared with using TBMs, with continuous productivity.

For better performance, the team has deployed state-of-the-art equipment like automatic and semi-automatic drill jumbos, continuous loaders, side dump wheel loaders, PLC controlled robo-arm shotcrete machines and truck mounted Grout Plants with onboard data loggers.
Defining & overcoming hurdles
For Claims & Contracts In-charge, Srimaan Nannapaneni, the challenges were about establishing secure and reliable communication inside the tunnels, keeping an eagle eye over the Rs. 200+ crores worth of assets deployed at the project and shutting the tap on fuel pilferage.

Communication: Hitherto only telephone intercom was available in tunnels with no internet access. “Our aim was to establish internet connectivity, improve communications and set up advanced monitoring systems inside the tunnels,” says Srimaan purposefully. Rolling up their sleeves, the team first studied detailed contract requirements, reviewed the communication systems available in other tunnels in India and Europe and collaborated with the corporate digital team to create a solution. Their first triumph was to set up a comprehensive tunnel communication system with internet connectivity (through OFC) along with a GPON (Gigabit Passive Optical Network) system to consolidate all the associated devices & services like internet, CCTV, VoIP, IP based intercom system, biometric devices onto a single fibre transport network. “We are connected inside all the 16 tunnel faces with speeds of up to 500 Mbps,” smiles Srimaan.
Video analytics: With the help of the tunnel communication system, the team implemented video analytics for real time monitoring, and automatically capture people and machine movement inside the tunnel. “Deployed in a tunnel perhaps for the first time, we have special face recognition cameras to capture people movement and high motion cameras to capture vehicle movement across all tunnel entry/exit locations,” adds Rajesh.
Bringing assets under the 3rd eye: Once the internet connectivity and monitoring systems (video analytics) were in place, the team shifted their focus to decide how to digitally cover their assets. Drill Jumbos have been fitted with WLAN devices and with the help of the tunnel communication system, data is transmitted to the desktops/laptops of engineers for monitoring. “We have installed PLC and HMI (Human Machine Interface) displays on all our eight shotcrete machines and connected them with various sensors,” shares Paramjit Singh, Head – Project Controls “After calibration, we generate job analysis reports and can calculate and corelate productivity and accelerator consumption too.”

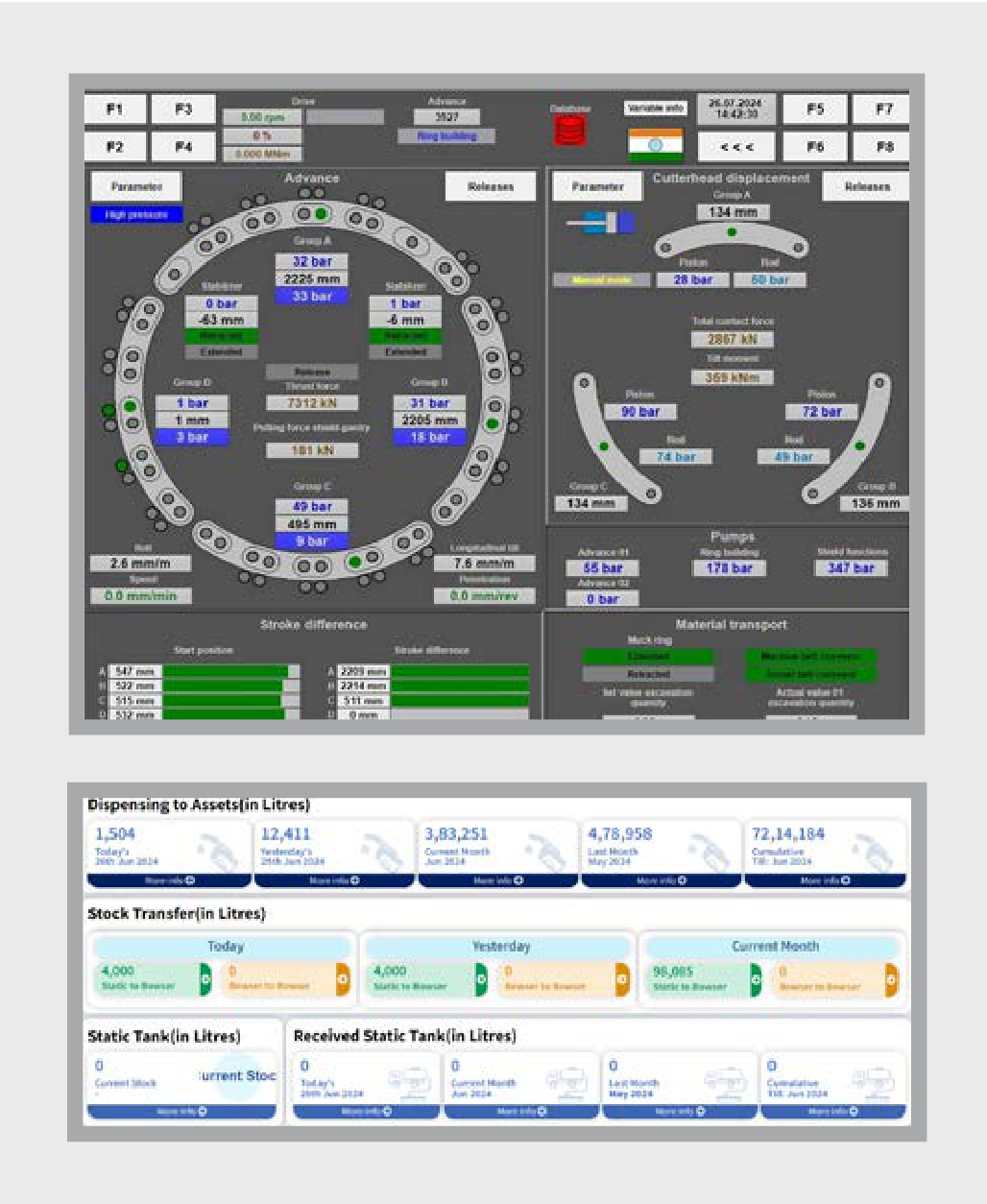
Digital fuel monitoring: The RVNL Package 2 is one of the earliest adopters of the digital fuel monitoring system covering the entire fuel chain system, right from fuel receipts till fuel consumption. Underground fuel level sensors have been installed on two 20 KL capacity underground tanks that record the fuel received from the supplier. A static dispenser installed with a RFID reader captures real time fuel issuance with reference to RFID tags; mobile bowsers are also equipped with RFID readers & GPS trackers to capture data of the fuel being dispensed to the equipment. Further, the fuel sensors, GPS sensors and IOT gateways installed on all owned, hired and subcontractor assets provide details of fuel receipt, average fuel consumption, GPS trail, fuel pilferage alerts, and more. “For real time monitoring of the entire chain, we have set up a war room to analyse, compare fuel dispensed as per bowser vs fuel receipt as per sensor, check for pilferage, record extra kms run for repairs, geofencing and immediately intimate concerned for necessary action,” elaborates Srimaan.

The RVNL Package 2 is one of the earliest adopters of the digital fuel monitoring system covering the entire fuel chain system, right from fuel receipts till fuel consumption.
Enjoying the fruits of digitalization
ROI on digitalization is really the proof of the pudding and Rajesh is happy with some of the results. “Thanks to our tunnel communication system and video analytics, the utilization of dumpers has jumped from 33% to 55%, transit mixer utilization improved by 7% and shotcrete rejection has reduced from 80 cum to just 15 cum.” Not surprisingly, their major savings are on the fuel front with short supply and pilferage coming down from the highs of 2,500 & 4000 litres per month to Zero. “Our recurring savings should be in the region of Rs. 10-12 lakhs per month by revising the fuel norms of key asset categories,” he smiles, “while the risk cost is to the tune of 5,600 litres per month i.e., about Rs. 5.43 lakhs/month by
restricting pilferage.”
The benefits have spread to other areas as well. On the delivery front, breakdowns are being promptly attended by troubleshooting with calls on WhatsApp video. “Consequently, we have observed that breakdowns have reduced by 2%,” smiles Paramjit. Realtime reporting of Drill Jumbos is leading to quick decision making and safety precautions.
In the ESG realm, carbon emissions can be communicated quickly to increase ventilation speed and at other times, the ventilation can be effectively optimized.
Another aspect that should please the site leadership is that near miss reporting time has improved from 30 minutes to real time with evidence and immediate action by top management. The client’s billing cycle time has also reduced by approximately 6 days.
RVNL Package 4
Tunnelling to a new high
A part of the larger 125-km long Rishikesh-Karan Prayag project, L&T’s RVNL Package 4 team under the leadership of Project Director, Rakesh Arora, is constructing two tunnels: 14.5 km upline and 13.1 km downline using both TBM and NATM methods, with two new, 9.1 dia. Single-shield hard rock TBMs (‘Shiv’ & ‘Shakti’), the largest deployed in the Himalayan region.

Although an uphill struggle, they have already completed various sections of the Escape & Main tunnels in Portals 1 & 2, substantial amount of excavation & lining work and over half of the planned excavation in both the upline and downline TBM tunnels. “We have completed 65% of excavation, that is 19.1 km out of the total scope of 29.5 km,” Rakesh says, nodding at their progress. “7,878 meters, (91%) of NATM excavation, 22% of the overt lining, covering 1,895 meters out of a total scope of 8,639 meters. 54% amounting to 11,229 meters of TBM tunnelling out of a scope of 20,786 meters have all been completed.” Not surprisingly, in the process, they have had to face some huge challenges.
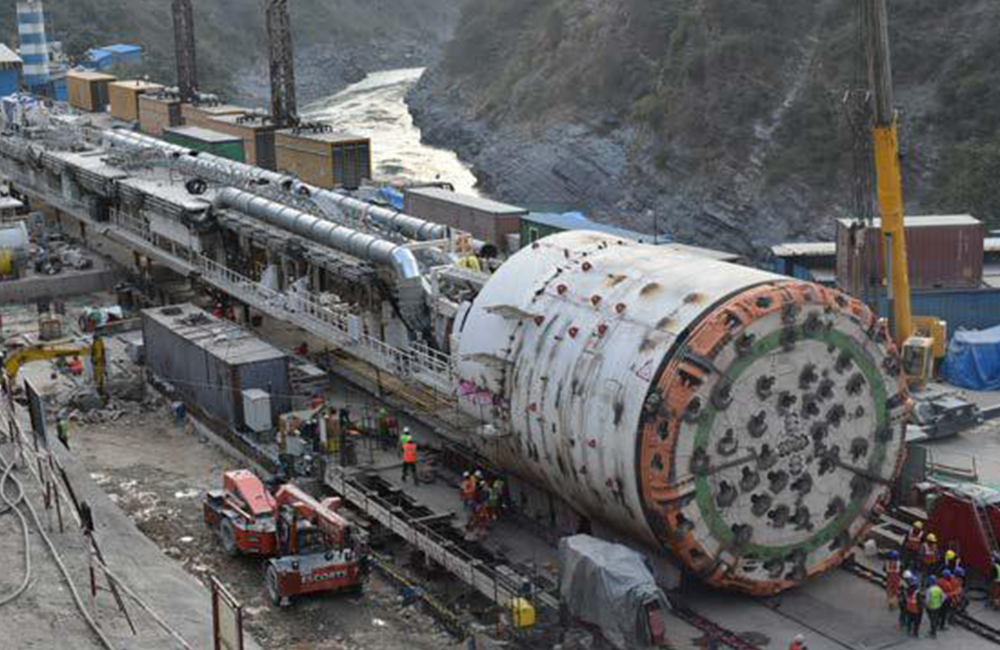

Moving mountains: Transporting the TBMs, imported from Germany in 110 consignments each, to site over hilly terrains, narrow roads, and untested bridges while overcoming highway restrictions on a combination of mechanical & hydraulic axle trailers and Self-Propelled Modular Transporters (SPMTs) has been a huge triumph. “Extensive planning, route surveys, and road widening helped us to overcome the logistical hurdles,” remarks Project Control Head, Shamim Ahmed. “We even conducted live load test of 240 MT (cargo + SPMT weight) on old bridges for three days to ensure that they support the heavy cargo.”

Assembling the TBMs: With 1,000 MT hydraulic gantry cranes with space-efficient, safer, self-propelled base frames and telescopic octagonal boom sections, constantly monitored by the Computer Assisted Remote Lifting (CARL) system, the team assembled the TBMs within strict timelines that involved handling huge weights, and constraints in sequential civil works. “Both the 140 m long TBMs were assembled in 6 weeks, saving us 4 weeks,” highlights Team Leader, Christopher Cooper, “and by using only one assembly area, other site activities could commence earlier.” Not only have they been recognized internally for this innovation, but their process has been adopted at other projects, such as Pakal Dul, J&K. “At the end, the entire process of transporting and assembling the TBMs was efficient & cost-effective,” rounds off a
pleased Chris.

Pushing & leveraging the TBMs: Once assembled, to push the two TBMs over distances of 600 & 700 m respectively, the team developed an in-house skid jack system featuring skid tracks, PTFE-coated skid pads, and hydraulic lifting jacks, that increased the speed of movement to an impressive 139 m per day. Chris is delighted with the improved operation efficiency and the 33% reduction in costs. “Additionally, it required less labour by eliminating the need for constructing and welding reaction frames, reducing the risk of welding-related injuries and its simplicity and feasibility ensured smooth implementation.” The process was completed in 14 & 8 days respectively as against the anticipated 30 days for each TBM.

Tunnel Seismic Prediction (TSP): “With TSP, we can analyse and predict ground conditions up to 100 m ahead of the TBMs compared to 30 m with traditional probe drilling,” points out Senior Geologist (TBM), Manoj Kumar, elaborating that TSP involves emitting seismic waves into the ground to measure reflected signals and create a detailed image of the geological structure to identify potential hazards such as water-bearing strata, faults, or unstable ground.
India’s first fully automatic carousel system: In a groundbreaking development, a fully automatic carousel system precasts segments for TBM tunnelling that automates the movement of moulds through various stations, including cleaning, oiling, cage fixing, insert fixing, concrete pouring, finishing, steam curing, and de-moulding. Each activity is precisely timed to 10 minutes, to ensure efficiency and adherence to the project schedule. An in-built auto cut steam chamber can store
42–44 segment moulds and maintain a curing temperature between 50°C and 65°C, which accelerates production by achieving a de-moulding strength of 25 MPa in just 8 hours, while separate flying buckets transport concrete, maintaining a workability slump of 75 ± 25 mm for optimal segment surface finish. Two identical factories produce 16–24 rings (8 segments per ring) and 20 invert segments daily enable the team to cast 20 rings a day, as against 12–18 rings possible with traditional methods.
Technology interventions to drive efficiency
“Our integrated digitalization efforts have enhanced communication, monitoring, and security,” explains Rakesh, “that include installing Wi-Fi access points throughout the tunnel, a leaky feeder system for seamless connectivity for various applications and devices and deploying 88 IP-based mobiles for real time communication between the team members in the tunnel.”
Recognizing some stalwarts driving technology adoption
Rakesh is breathing easier largely due to the effort of some stalwarts in his team like Sunil Dutt Vats (Project Manager – NATM), handling Execution & Operations, who has played a key role to complete the tunnel excavation works by NATM technology to launch the TBMs ahead of schedule. His expert management of logistics to transport the precast segments and remove the excavated muck has been crucial for the undisturbed operation of the TBMs.
Making his presence felt is Sunil Kumar Gupta (Deputy Project Manager – NATM) to set up and maintain the Portal-2 Area including Ventilation Shaft; his close supervision of the tunnel construction works by NATM technology and the works at the precast segment yard have ensured encouraging progress.
While Project Manager – TBM, Himanshu Arora’s management of the TBM team and progress of works on the TBM front has resulted in a record-breaking performance, Construction Manager – TBM Front, Mayank Bajpai, has contributed his bit to execute the civil works and support the continuous mining by the TBMs.
Workers: Apart from biometric attendance systems & CCTV cameras, the team’s Workmen Application System helps to plan manpower, monitor their quantity of work, and assess productivity on a daily and monthly basis. “Our Workmen Management System centralizes management by providing real-time data and analytics, automating onboarding, and managing entry/exit with security protocols,” shares Accounts and Admin Head, Chandragupta Patra, “which enhances productivity, ensures compliance, and supports decision-making with custom reports and data analysis.” The Workmen Allocation System Dashboard tracks daily and monthly attendance (presently, 2,450), generates various detailed reports, jobwise and shift-wise monthly reports, location-based reports, and comparisons between approved and actual workmen. Additionally, it highlights unprocessed attendance records, in-time logs, and deviations from standard
time-watching procedures.

Achieving efficiency in fuel dispensing: With accurate real-time data, Fuel Level Sensors, the team is effectively managing fuel, achieving operational efficiency, & saving costs, preventing fuel theft, and ensuring timely refuelling. When the tagged equipment approaches the dispenser, RFID readers scan the tag to verify authorization to dispense fuel that ensures accurate diesel dispensing to the equipment and prevents fuel pilferage & misuse. According to previous data from various projects and surveys from different websites, general pilferage rate is 10%; by deploying this LLS system they have reduced fuel consumption by 10% which amounts to approximately INR 9.4 Crores. Additionally, by preventing fuel pilferage, there is further savings of INR 8 lakhs.
HK Connect: “We use Herren Knecht’s TBM connected software to monitor and analyse key parameters and performance of our two TBMs,” informs Himanshu Arora, “for real-time insights through comprehensive dashboards and detailed sensor data evaluations.” The system enables remote jobsite and project management, automatic analysis and better
decision-making.
ISETIA: A globally trusted cloud-based platform for efficient process and project management, ISETIA supports comprehensive planning, execution, and reporting of programs, projects, and portfolios offering multilevel, personalized management with modules including Document Management, 3P Management, Cost Management, Process Management, Risk Management, Issue Management, Change Management, Lessons Learned, and BIM Viewer. The ISETIA Analytic module improves decision-making with powerful BI reports and dashboards, providing data-driven insights and strategic management of projects at all levels.
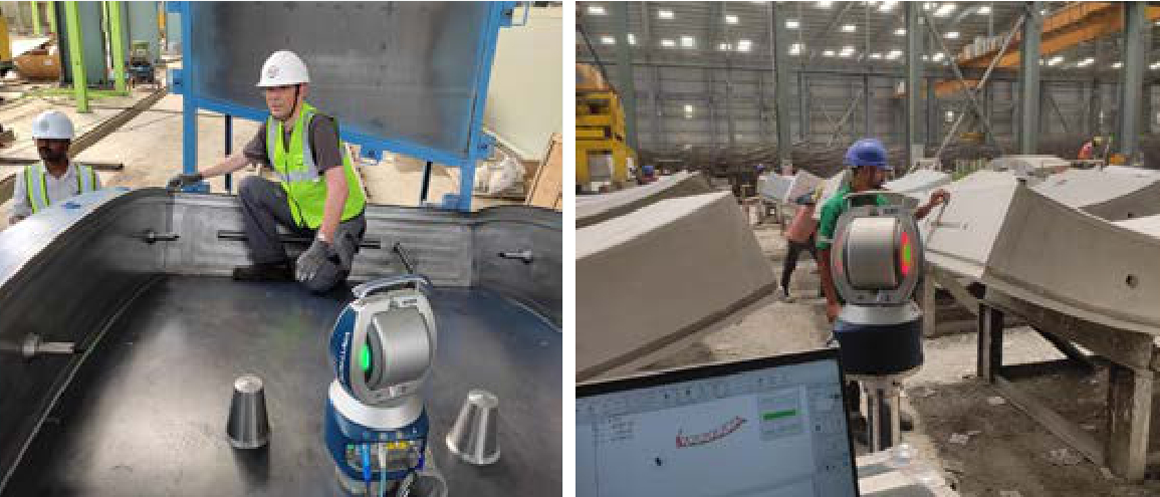
Segment Documentation System (SDS): Given the distance of 26 km from the casting yard to the TBM site and a stock of over 1,200 rings, it is crucial to track each segment accurately and with SDS, each mould is uniquely identified to track the segments through every stage of the process: from cage fixing, casting, primary stacking, transportation to the TBM site, secondary stacking, and finally, transportation to the TBM and erection in the tunnel. The SDS system meticulously records reinforcement cage identification, casting date and time, vibration duration, concrete quantity, temperature, de-moulding, transportation, and erection details, ensuring comprehensive monitoring and quality control throughout each
segment’s journey.
Laser Tracker: Accurate checks are carried out using the German-engineered FARO Laser Tracker to measure dimensions up to two decimal points in mm to accurately gauge contact joint angles, adhering to tight specification tolerances. Operated typically by one or two skilled personnel, these reports maintain the integrity of the tunnel segments during erection, minimizing lips, steps, and gaps.

Communication: A leaky feeder system ensures continuous communication underground in long tunnels, enhancing productivity and progress. An IP-based intercom system / mobile app intercom (fully Wi-Fi zone) connects every site/ tunnel under one location in real time, while server-based IP phones can monitor devices remotely.
While the ConEase App manages data for concrete requirements versus actual production per activity, recording time and location to reduce unnecessary site wastage, the Rebar Pro App helps minimize TMT wastage by optimizing the use of offsets and maintaining records of the reconciliation purposes. Key equipment such as Wi-fi-connected 84 CCTV cameras, P2P and RF devices ensure comprehensive surveillance and monitoring while GWN Cloud provides a single dashboard to oversee all these devices, for real-time monitoring and quick troubleshooting.
The RVNL project is set to redefine railway tunnel construction in India and Rakesh and his team of engineers and workers are doing more than their bit, helped along with their entire suite of digital solutions.